近日,我组在乳铁蛋白的结构质谱表征和质量控制研究方面取得新进展,建立了整合非变性质谱(nMS)和糖基化蛋白组学的乳铁蛋白活性结构和糖基化异质性表征新策略,实现了不同奶源乳铁蛋白的质量差异精准评估。

乳铁蛋白是母乳中的多功能活性糖蛋白,具有提高婴儿免疫力等重要生物活性。目前,牛乳来源的乳铁蛋白是婴儿配方奶粉、功能食品中的重要活性添加剂,对乳铁蛋白生产和运输中的质量控制尤其重要。当前工业化生产中采用色谱等手段对乳铁蛋白的的纯度进行控制,难以提供活性结构和糖基化异质性等与其生物学功能密切相关的分子信息。
本工作通过整合nMS和糖基化蛋白组学方法,对不同奶源和不同热处理加工条件下的乳铁蛋白的纯度、分子量、活性结构稳定性、糖基化异质性和抗菌活性等进行了系统表征。研究结果发现来自不同奶源的乳铁蛋白糖基化位点基本一致,但在位点的糖型上具有很高的微观异质性,例如N252和N564位点由高甘露糖型组成,而N300和N495位点主要包括唾液酸化和岩藻糖基化糖型。此外,结合nMS中的活性乳铁蛋白电荷态分布模式和尺寸排阻色谱-非变性质谱(SEC-nMS)分析中的定量峰强度,可以实现对不同加工工艺中乳铁蛋白结构稳定性的定量评估,相关质谱结果与其抗菌活性呈正相关。总体而言,nMS整合糖基化蛋白质组学策略可在分子水平上精准评估乳铁蛋白的纯度、分子量、糖基化异质性和活性结构稳定性,有望成为功能食品和药物用途的高品质乳铁蛋白生产过程中的全新质控策略。
相关研究成果以“Assessment of the Conformation Stability and Glycosylation Heterogeneity of Lactoferrin by Native Mass Spectrometry”为题,于近日发表于食品领域顶级期刊Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry。该工作的共同第一作者是我组联合培养硕士研究生慕宇和工程师赵姗。该项目获得国家自然科学基金、呼和浩特科技计划、国家乳业技术创新中心开放基金的资助。(文/图 慕宇)

Figure 1. Schematic diagram of the nMS characterization of the conformation stability and glycosylation heterogeneity of LTF.
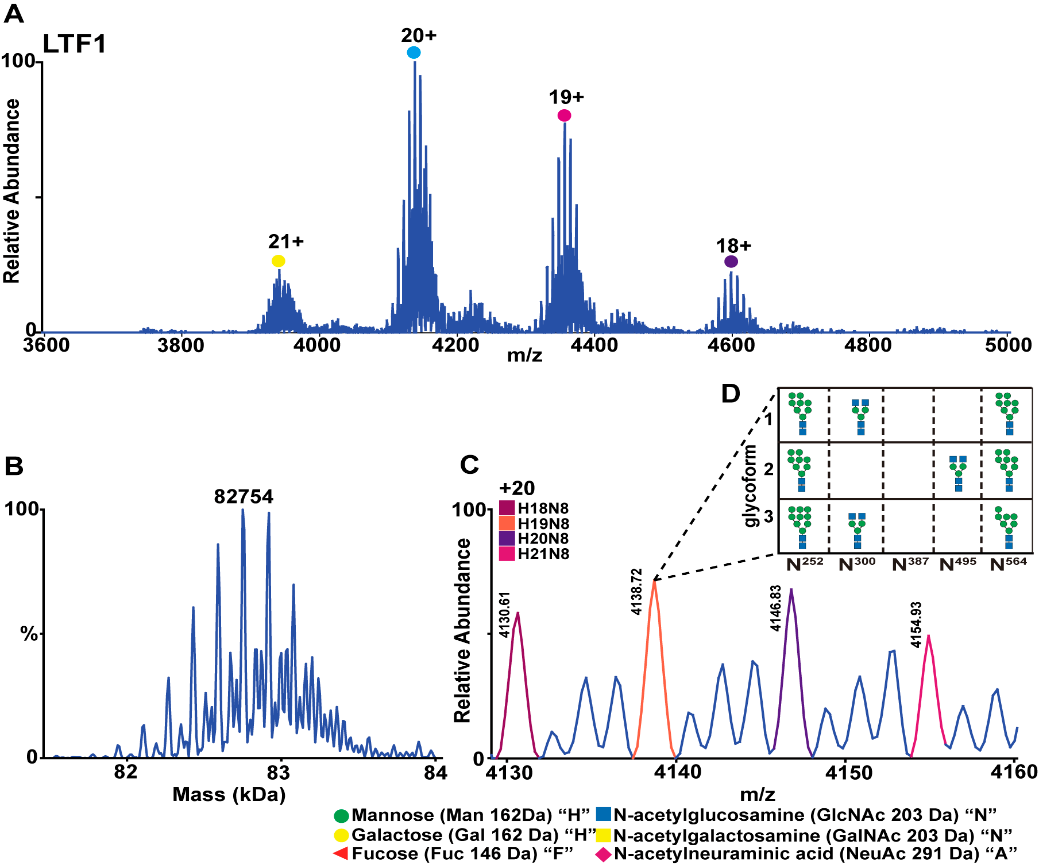
Figure 2. NMS characterization of LTF1 (A), MW measurement after deconvolution (B), distribution of different N-glycans in LTF1 (C), and compositions of the three site-specific glycan combinations matching the most abundant LTF1 form (m/z 4138.72) in nMS (D).
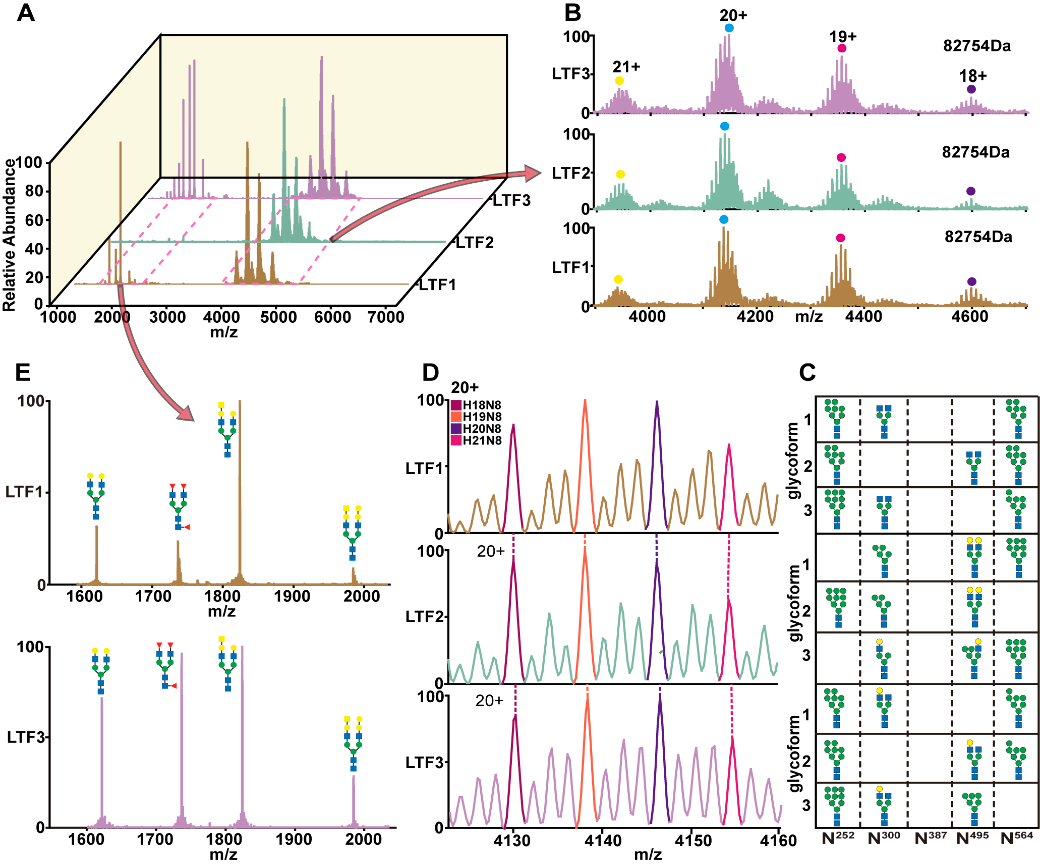
Figure 3. NMS spectra of LTF1, LTF2, and LTF3 (A); the charge state distributions and proteoform patterns (B); the combinations of top 3 potential glycan structures of the dominant LTF forms in nMS (C); the distribution of different N-glycan types (D); and the potential structures of degraded glycans from LTF1 and LTF3 (E)
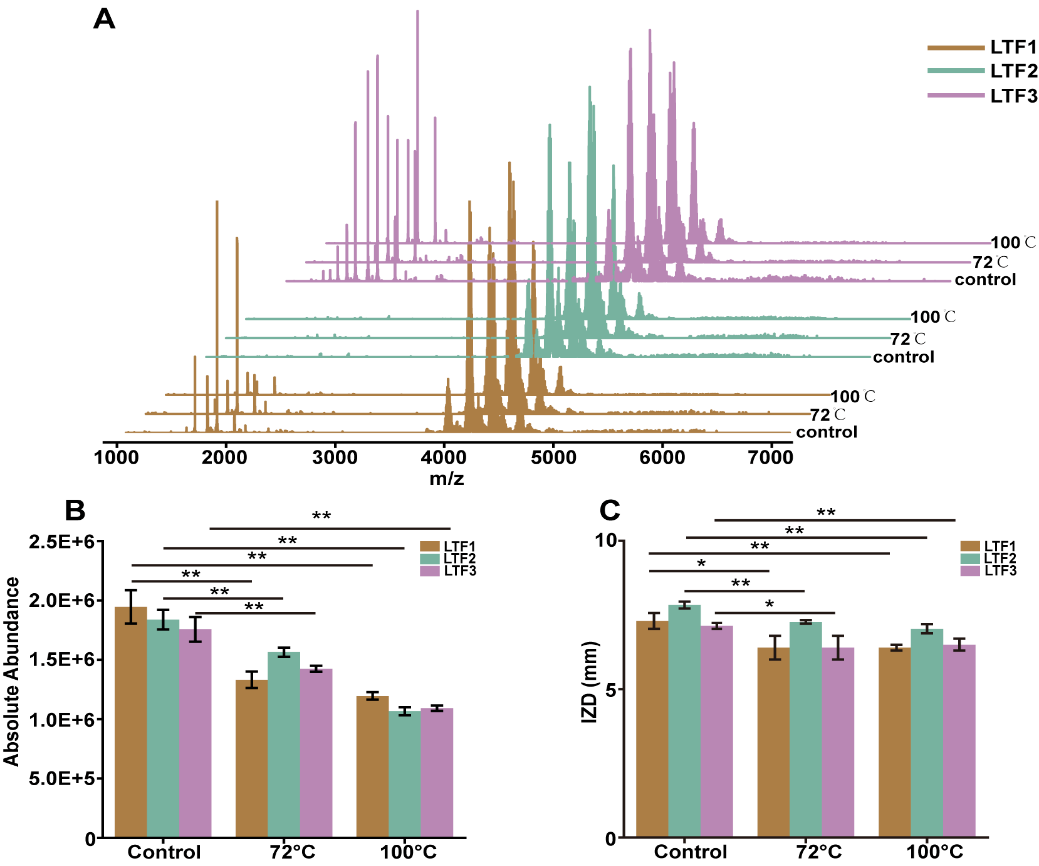
Figure 4. NMS spectra of LTF1, LTF2, and LTF3 under transient high-temperature treatment conditions of 72 °C for 15 s and 100 °C for 10 s (A); quantitative peak intensities (B) and antimicrobial activities (C) of LTF1, LTF2, and LTF3 under different treatments. The three LTF samples against E. coli were measured at 50 mg/mL. * when p < 0.05 and ** when p < 0.01.

